
Inorganic Chemistry of Main Group Elements. (2003). “The Place of Zinc, Cadmium, and Mercury in the Periodic Table”. The majority of manufactured products contain these elements. The main group elements and their compounds are among the most economically important elements.
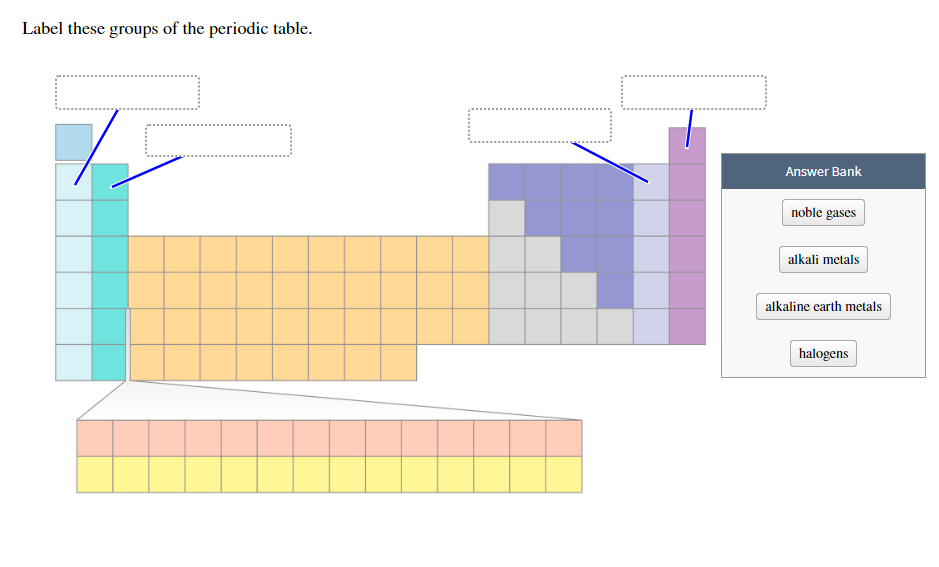
Biological molecules require main group elements, particularly carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus. These elements are critical for supporting life.For this reason, the main group elements are also called the representative elements. The main group elements, along with a few light transition metals, are the most abundant elements in the universe and on Earth.The main group elements are important for a few reasons: P-block elements include nonmetals, metalloids, and metals, so their properties depend on their group.Their valence electron is in the p orbital. The general oxidation state of p-block metals is ns 2 np 1–6.The group 17 elements (halogens) have an oxidation state of -1, while the group 18 elements (noble gases) have an oxidation state of 0. But, oxidation state and other properties depend on the group.For example, the oxidation states of sulfur are -2, 0, +2, +4 and +6. The p-block elements are characterized by having multiple oxidation states, often separated by two units.Most of the s-block elements impart color to a flame.They form ionic compounds with nonmetals. S-block metals are highly electropositive.The s-block metals tend to be soft, with low melting and boiling points.With the exception of helium, all s-block elements are highly reactive.Group 2 elements (alkaline earth metals) have a +2 oxidation state. Group 1 elements (alkali metals) have a +1 oxidation state.Their general valence configuration is ns 1–2.The s-block elements have one oxidation state.Main group element properties depend on whether they are s-block or p-block elements: S-Block Element Properties A few scientists include the group 3 elements (scandium and yttrium) and sometimes the lanthanides and actinides. Some scientists believe the group 12 elements (zinc, cadmium, and mercury) should be included as main group elements because they share common properties with the elements to the right of them on the table. Sometimes the element hydrogen (atomic number 1) is excluded as a main group element.
Some people don’t include the superheavy elements from meitnerium (atomic number 109) to oganesson (atomic number 118) because too few atoms have been synthesized to verify their properties and because these properties are heavily influenced by relativistic effects. Examples of main group elements include helium, lithium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon.Įlements that are not main group elements are the transition metals (such as titanium, copper, and gold), the lanthanides (such as lanthanum and erbium), and the actinides (such as actinium and plutonium). The p-block elements are the basic metals, metalloids, nonmetals, halogens, and noble gases. The s-block elements are the alkali metals and alkaline earth metals. When the periodic table is divided in this manner, the other main element categories are the transition metals and the inner transition metals. In older IUPAC group numbering systems, the main group elements are groups IA, IIA, and IIIA to VIIIA. These are elements in group 1 and group 2 (s-block) and groups 13 through 18 (p-block). The main group elements are the chemical elements belonging to the s-block and p-block on the periodic table. The main group elements are groups 1, 2, and 13-18 on the periodic table. This entry was posted on Septemby Anne Helmenstine (updated on June 23, 2021)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
